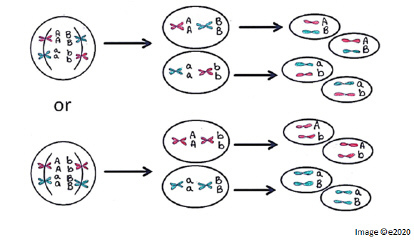
- Transformation: is the process by which a bacterial cell takes up free DNA from its surrounding environment. This external DNA can then be incorporated into the bacterial genome, potentially altering the bacterium's genetic makeup.
- Conjugation: This occurs when two bacteria physically connect through a structure called a pilus, allowing the transfer of genetic material (usually plasmids) from one bacterium to another.
- Transduction: In this process, a bacteriophage (a virus that infects bacteria) transfers DNA from one bacterium to another as part of its infection cycle.
![illustrat digram]()
Read More- Which Choice Best Describes the Purpose of Most Pharmacogenomic Research?